Fiber optic cables and their structure
Fiber optic cables play a crucial role in modern communication networks, offering fast and reliable data transmission. They consist of three main components and are available in several structures suited to different uses. In this article, discover in detail these components and the various structures of fiber optic cables.
The 3 components of fiber optics:
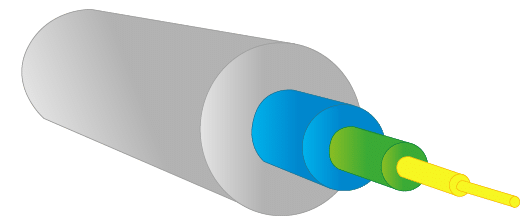
The core: made of silica, molten quartz, or plastic, in which optical waves propagate. Diameter: 50µm or 62.5µm for multimode fiber and 9µm for single-mode.
The optical cladding: generally made of the same materials as the core but with additives, which confine the optical waves to the core.
The primary coating: a protective plastic coating that ensures the mechanical protection of the fiber.
The different structures of fiber optic cables:
SIMPLEX

A simple and robust construction, ideal for basic installations.
- Fiber optic
- Tube from 700 to 900µm
- Reinforced with aramid yarns
- Outer sheath LSZH or PVC Ø 1.6 to 2.8mm with identification markings and metric scale
ZIPCORD

Used for pair connections, often for internal connections.
- Fiber optic
- Tube from 700 to 900µm
- Reinforced with aramid yarns
- Outer sheath LSZH or PVC Ø 2×1.6mm to 2×2.8mm with identification markings and metric scale
DUPLEX

Ideal for bidirectional connections in professional environments.
- Fiber optics
- Tube from 700 to 900µm
- Reinforced with aramid yarns
- LSZH sheath from 1.6 to 2.8mm
- Outer sheath (over the sheath) LSZH or PE with identification markings and metric scale
BREAKOUT

Perfect for installations requiring multiple connections with enhanced protection.
- Central dielectric reinforcement
- Reinforced with aramid yarns
- Tear-resistant film
- Fiber optics
- 900µm tube
- Colored LSZH cordage sheath at 2mm
- Outer sheath (over the sheath) LSZH with identification markings and metric scale
DISTRIBUTION
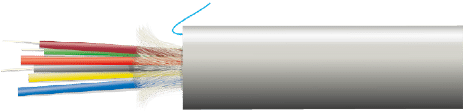
Used for star connections in complex environments.
- Fiber optic
- Colored 900µm tube
- Protective reinforcement with fiberglass
- Outer sheath LSZH or PE with identification markings and metric scale
- Tear-resistant filament
CENTRAL LOOSE TUBE
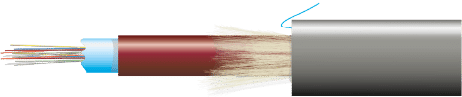
Optimal choice for outdoor installations with a large fiber capacity.
- Colored fiber 250µm
- Filling gel
- Protective reinforcement with fiberglass
- Outer sheath (over-sheath) LSZH or PE with identification markings and metric scale
- Central tube
- Tear-resistant filament
MULTITUBE

An effective solution for high-density fiber installations.
- Number of fibers: from 36 to 144 fibers
- Components:
- Central dielectric reinforcement
- Filling gel
- Tube containing 12 colored fibers 250µm
- Outer sheath LSZH or PE
MICROMODULE

Perfect for large installations with flexible fiber management.
- Number of fibers: from 12 to 864 fibers
- Components:
- Colored fiber 250 µm
- Flexible sheath containing the fibers
- Easy stripping
- Outer sheath LSZH or PE with fiberglass reinforcement
TIGHT STRUCTURE

Flexible and robust, ideal for internal patch cables.
A plastic sheath is applied directly over the optical sheath. This type of structure mechanically strengthens the fiber and provides the flexibility needed for making patch cords or cables inside buildings.
LOOSE STRUCTURE

Suitable for inter-building connections with fiber protected by a tube.
One or more fibers are placed “free” inside a tube. This type of fiber is particularly used for inter-building connections.
To learn more: discover how to choose your fiber optic cable.
Order your fiber optic cable on our website 👇
Need more details about fiber optic cables?
Contact us for more information, our fiber optic experts will respond to your needs as quickly as possible:
contact@folan.net
+33 (0)4 78 800 810



